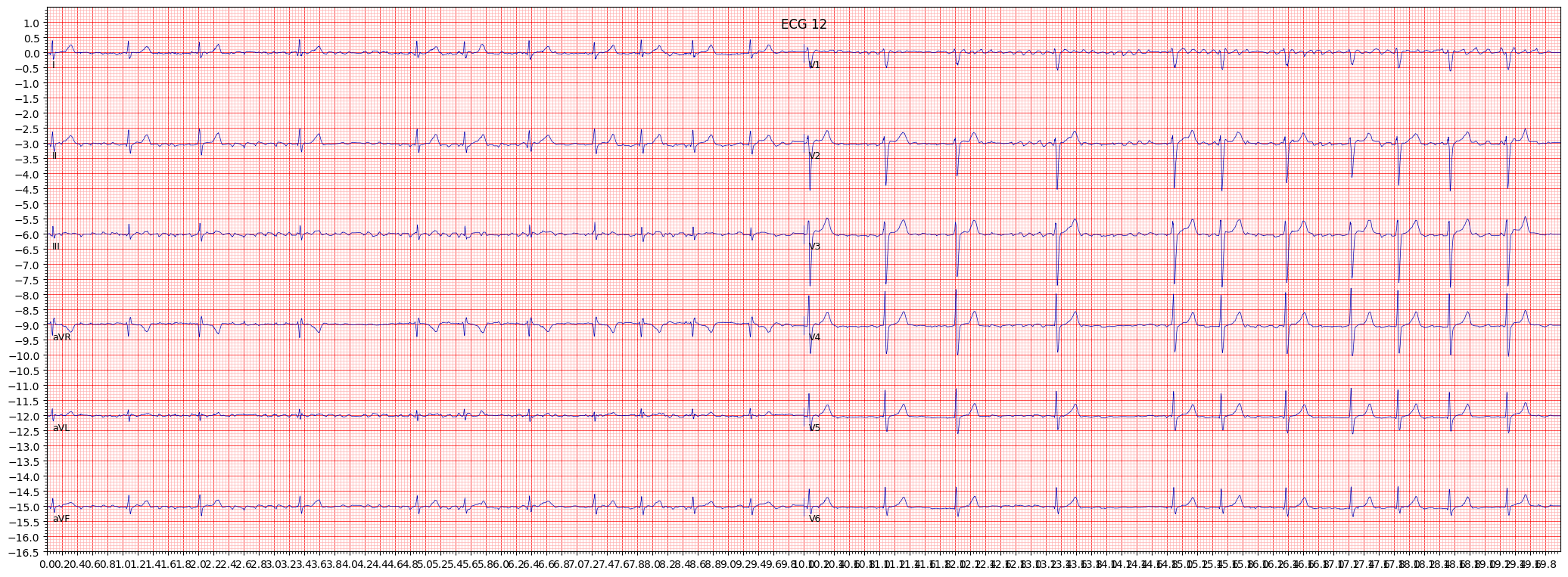
atrial fbrillation (AFIB)
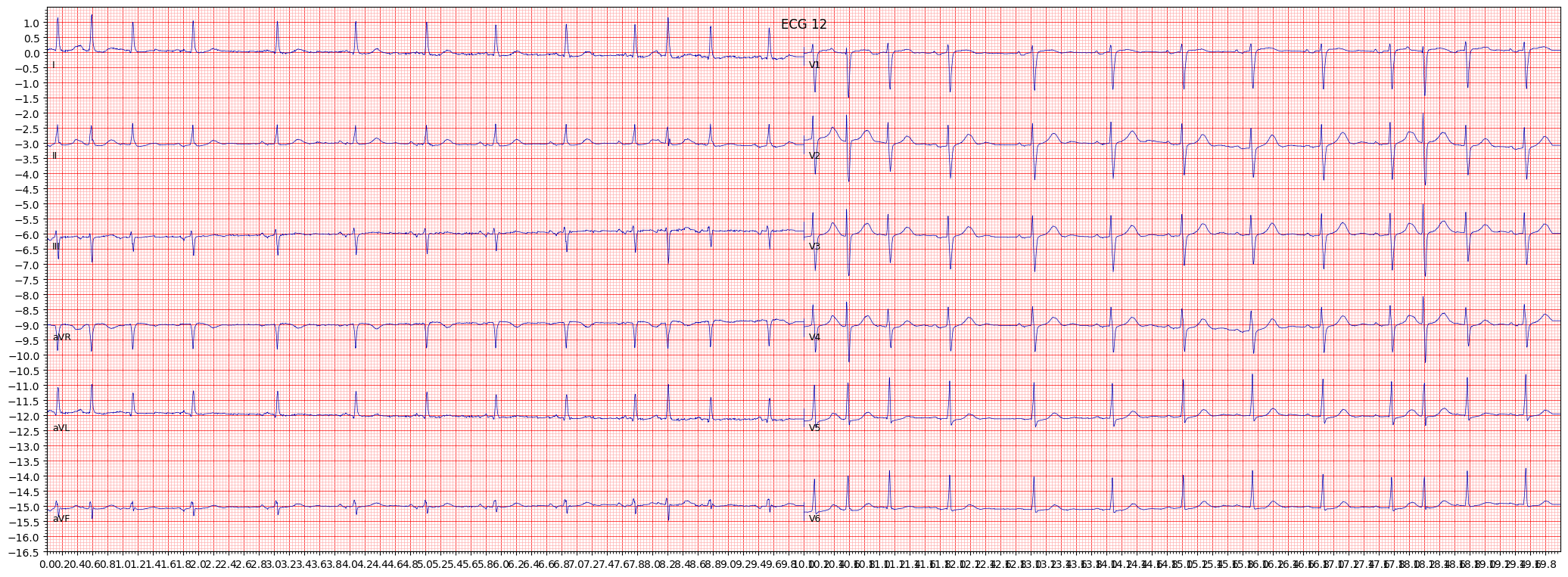
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm disorder that occurs when the atria, the two upper chambers of the heart, beat irregularly and out of sync with the ventricles, the two lower chambers of the heart. This can result in poor blood flow and oxygenation to the body, and increase the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular conditions.
Common symptoms of AFib include palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, weakness, fatigue, and dizziness. However, some individuals may not experience any symptoms.
When reviewing an ECG for AFib, it is important to pay attention to the absence of P waves and the presence of irregularly irregular QRS complexes. Other things to pay attention to include the presence of ST segment and T wave abnormalities and the heart rate.
- Look for the absence of P waves
- Check for the presence of irregularly irregular QRS complexes
- Observe the presence of ST segment and T wave abnormalities
- Examine the heart rate
If AFib is suspected, further testing such as echocardiography or cardiac MRI may be recommended to evaluate the structure and function of the heart. Treatment may include medications such as anticoagulants to reduce the risk of stroke and rate and rhythm control medications to manage the heart rate and rhythm.
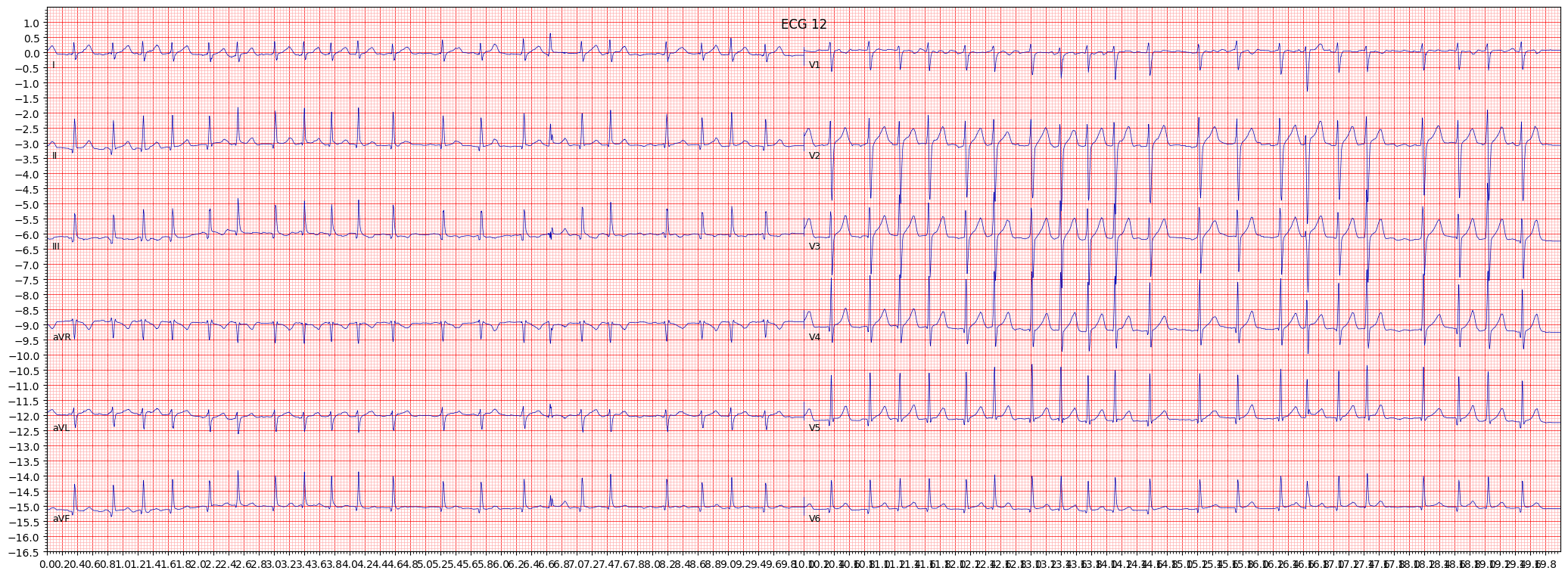 example 2:
example 2:
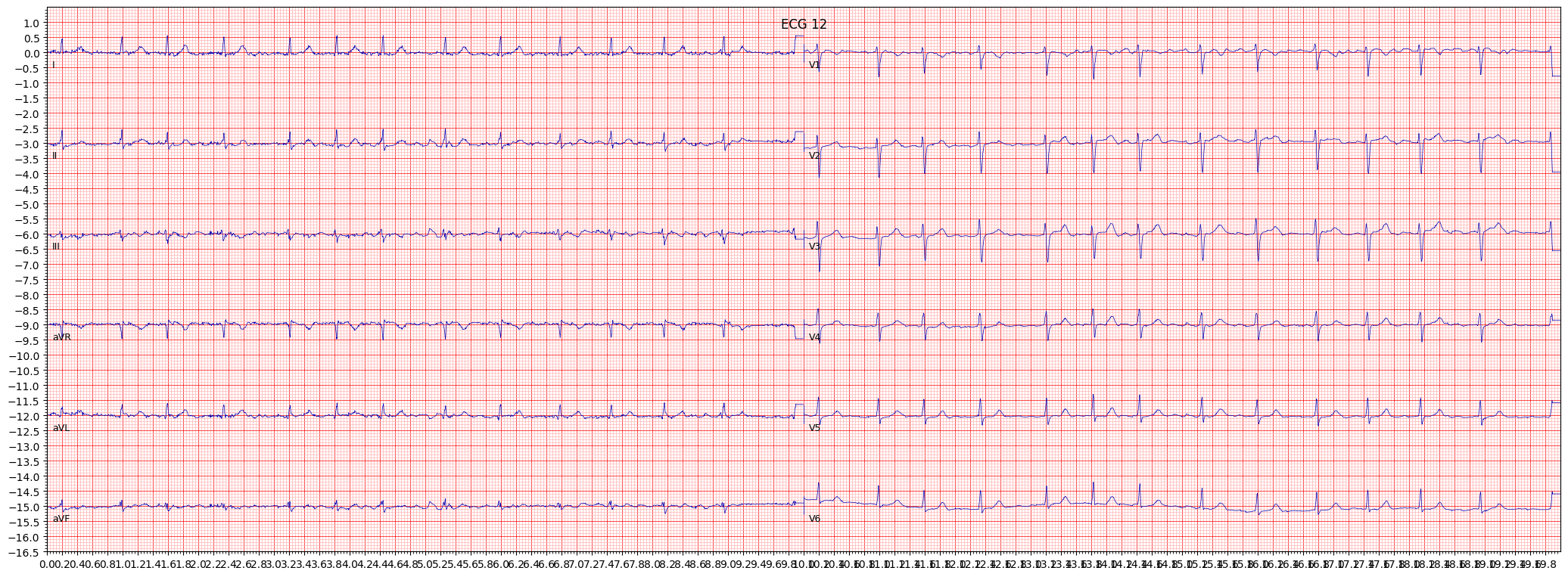 example 3:
example 3:
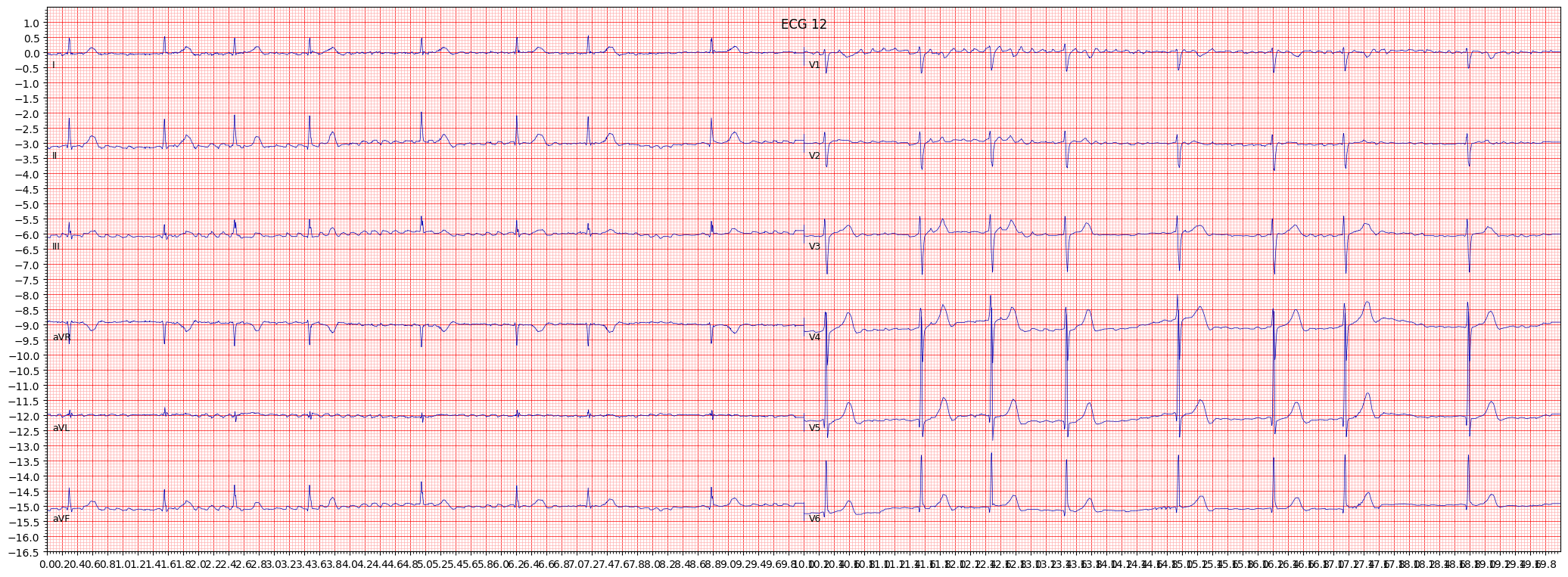 example 4:
example 4:
 example 5:
example 5:
 example 6:
example 6:
 example 7:
example 7:
 example 8:
example 8:
 example 9:
example 9: