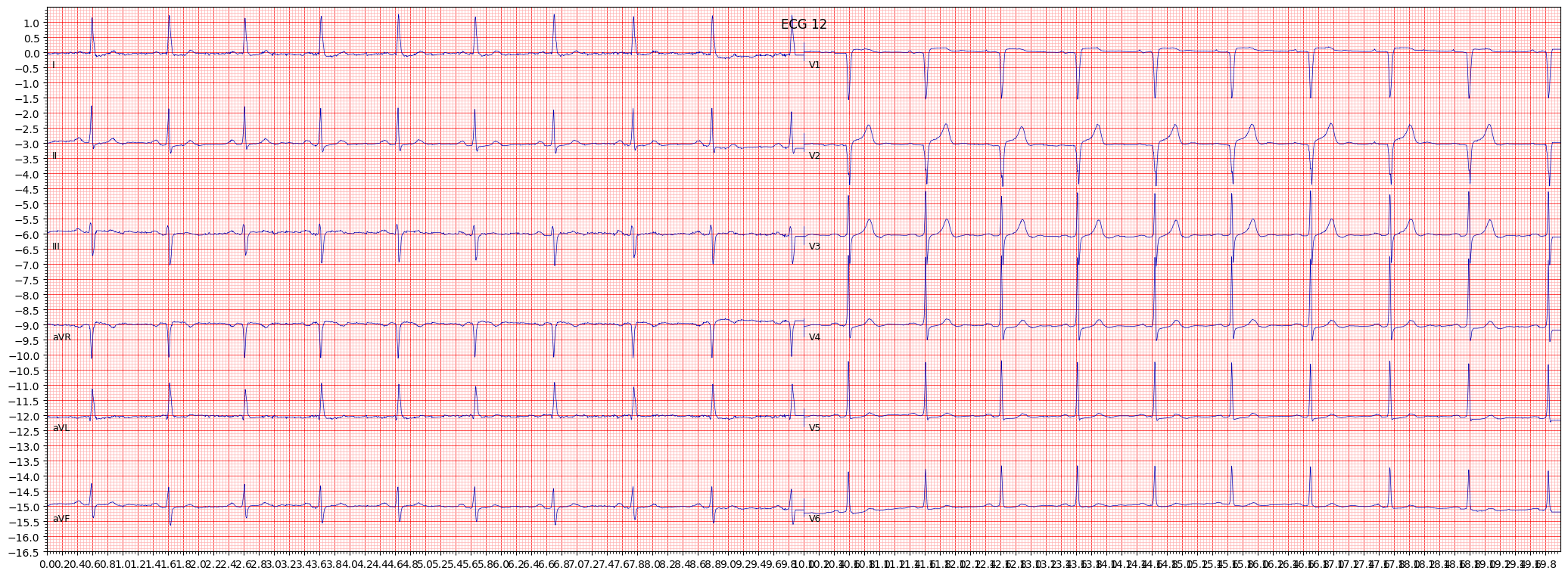
anterior myocardial infarction (AMI)
Anterior myocardial infarction (AMI) is a serious condition that occurs when there is a blockage in one of the arteries that supply blood to the front of the heart, resulting in damage to the heart muscle. This condition can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, and even death if left untreated.
Common symptoms of AMI include chest pain or discomfort that may radiate to the neck, jaw, shoulder, or arm, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and vomiting. However, some individuals may not experience any symptoms.
When reviewing an ECG for AMI, it is important to pay attention to the presence of ST segment elevation in the anterior leads, specifically leads V1-V4. Other things to pay attention to include the presence of Q waves in the anterior leads and T wave inversion in the lateral leads.
- Look for ST segment elevation in the anterior leads (V1-V4)
- Check for the presence of Q waves in the anterior leads
- Observe the presence of T wave inversion in the lateral leads
If AMI is suspected, emergency medical attention should be sought immediately. Treatment may include medications such as aspirin, nitroglycerin, and thrombolytic agents to dissolve the blood clot causing the blockage, as well as angioplasty and stenting or coronary artery bypass surgery to restore blood flow to the affected area of the heart.
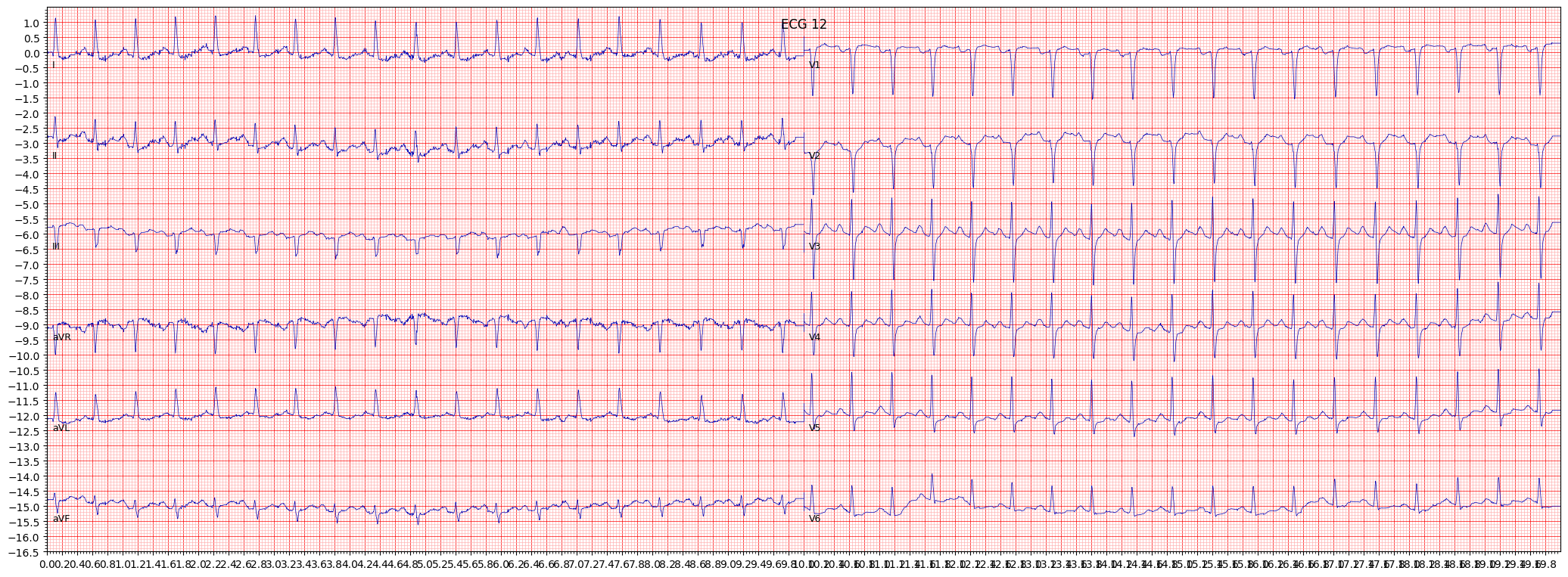 example 2:
example 2:
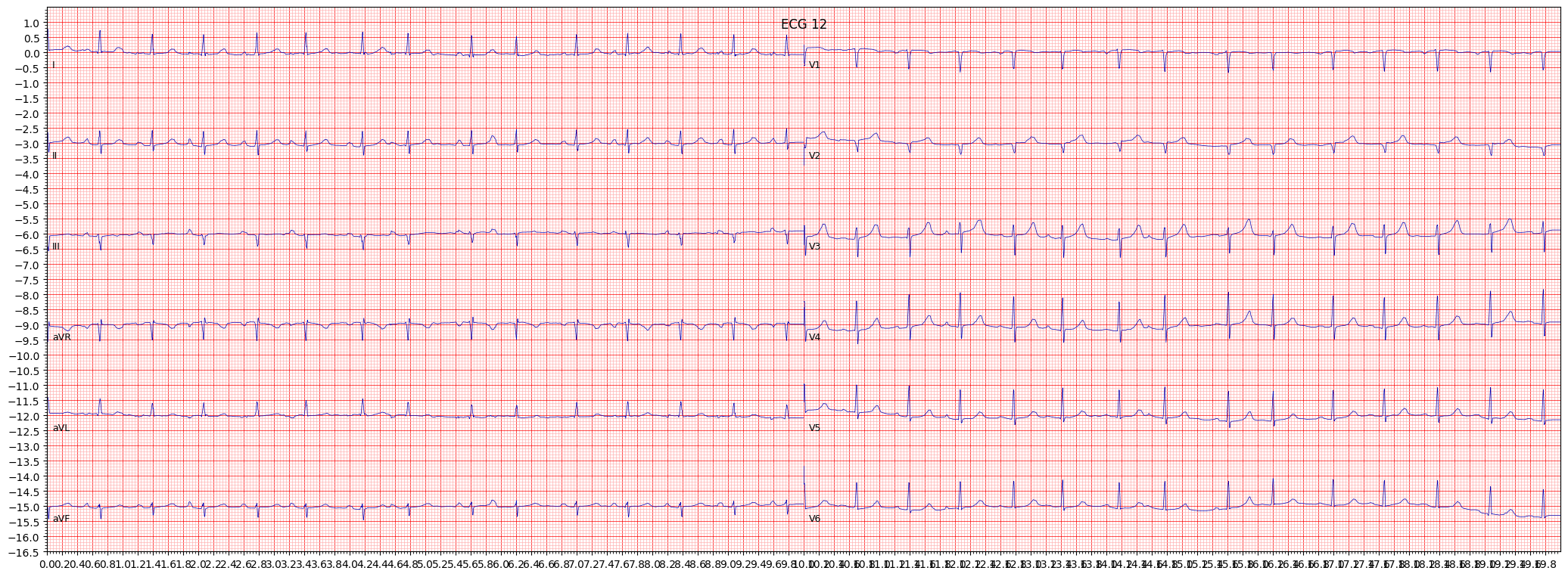 example 3:
example 3:
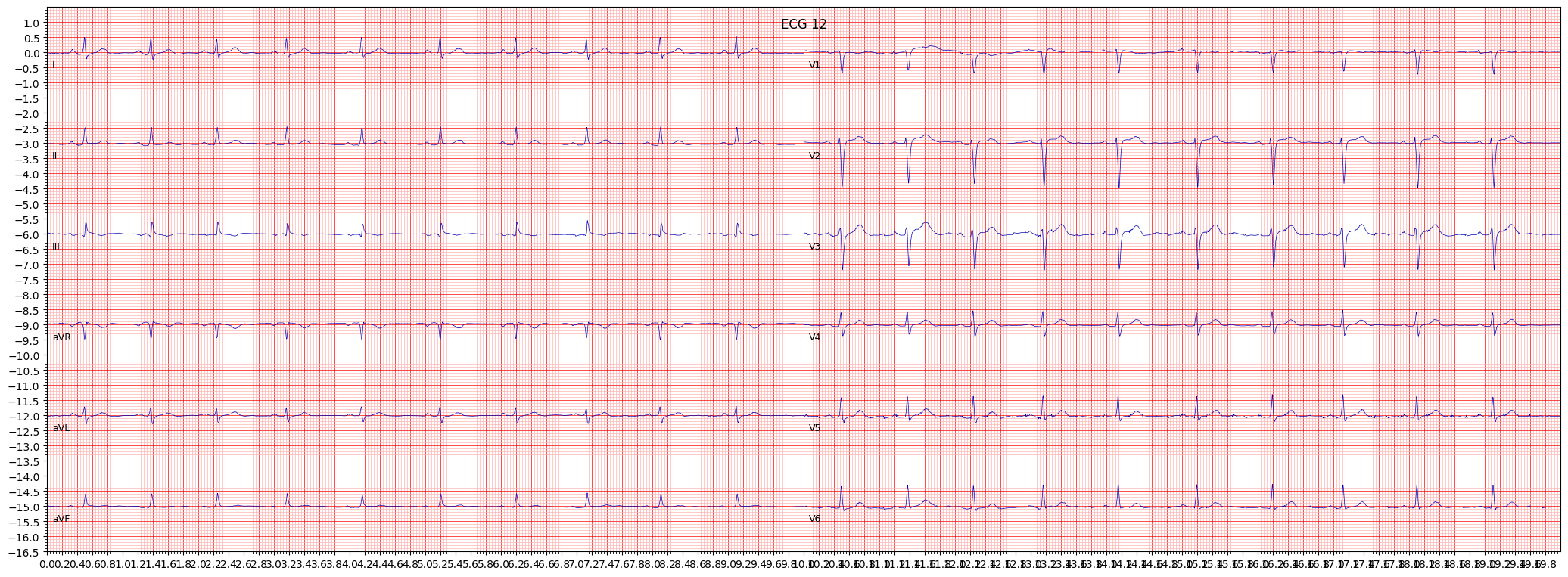 example 4:
example 4:
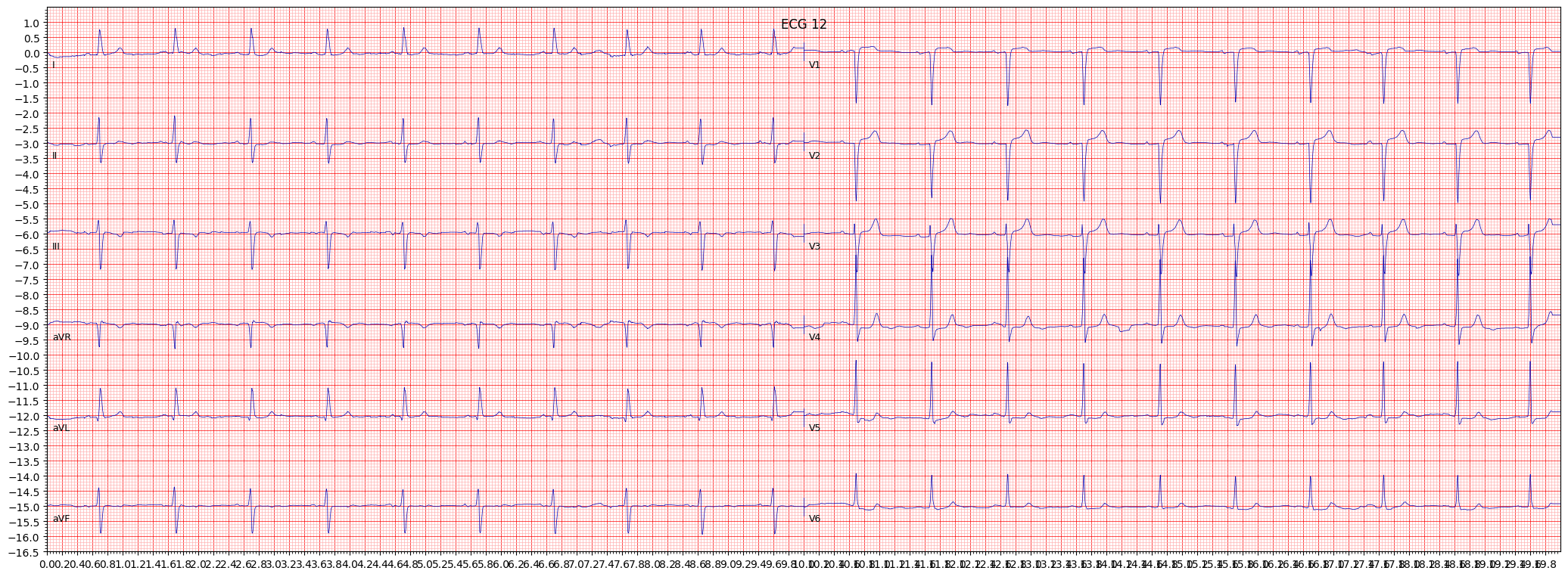 example 5:
example 5:
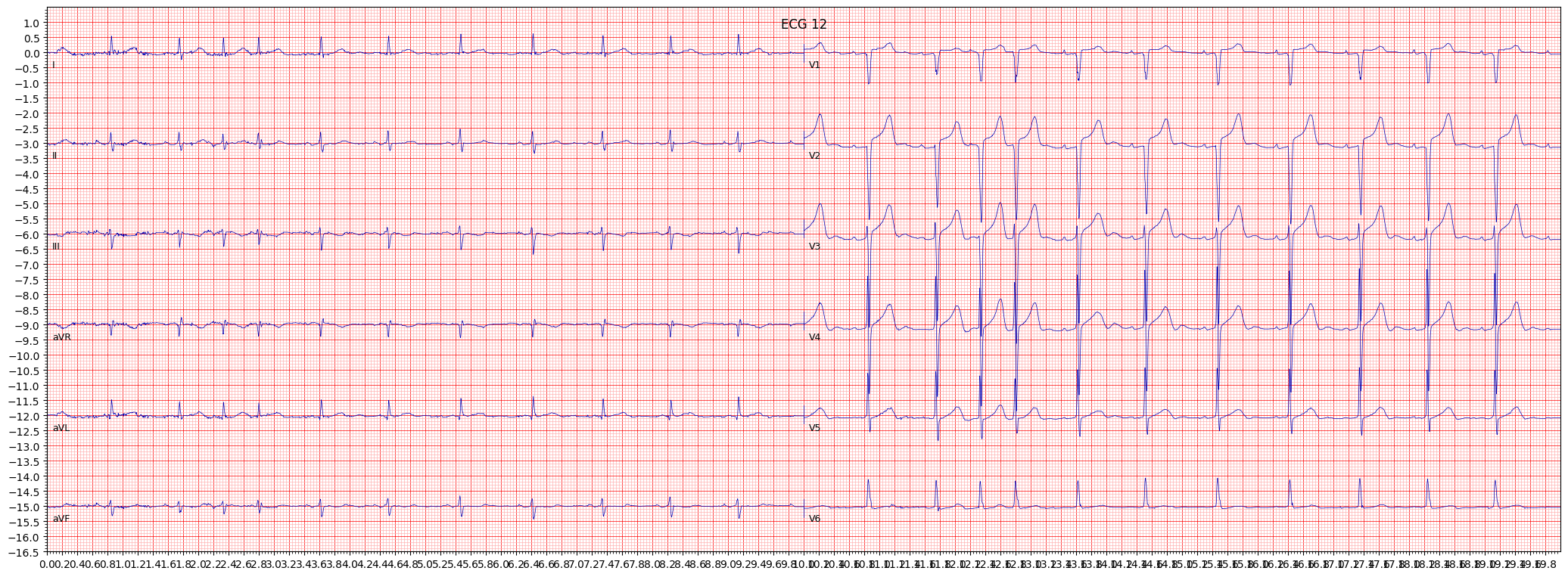 example 6:
example 6:
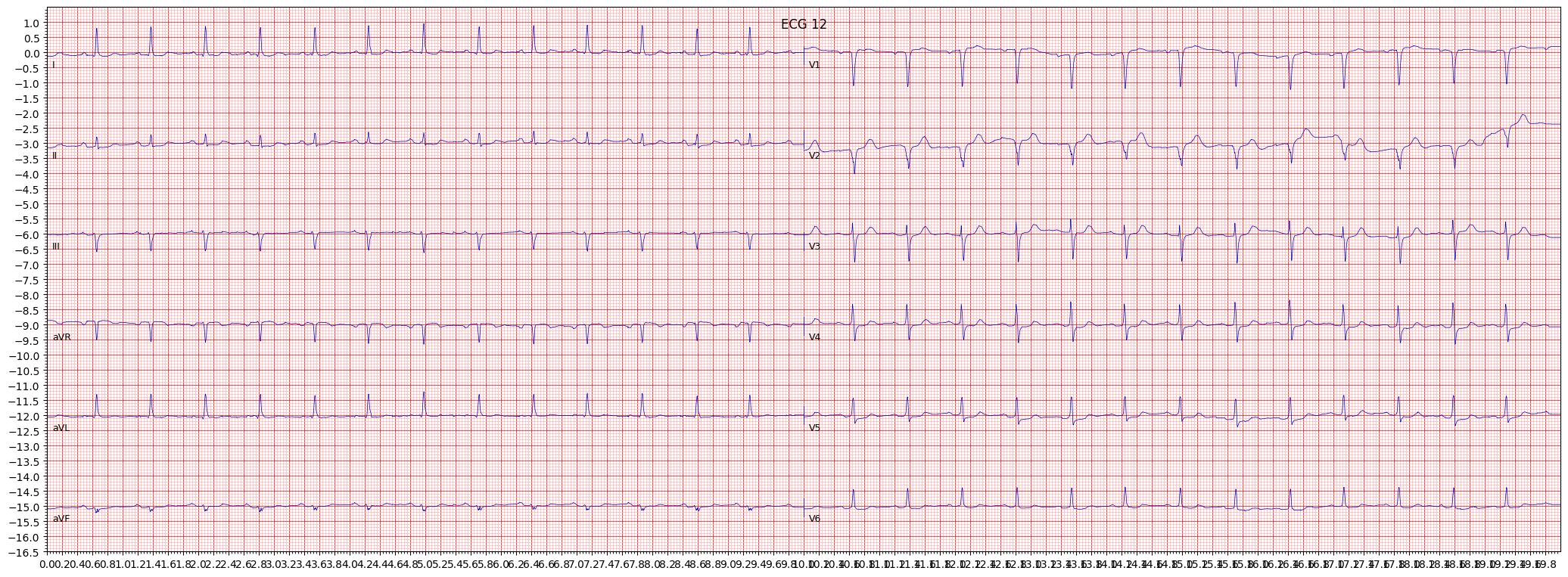 example 7:
example 7:
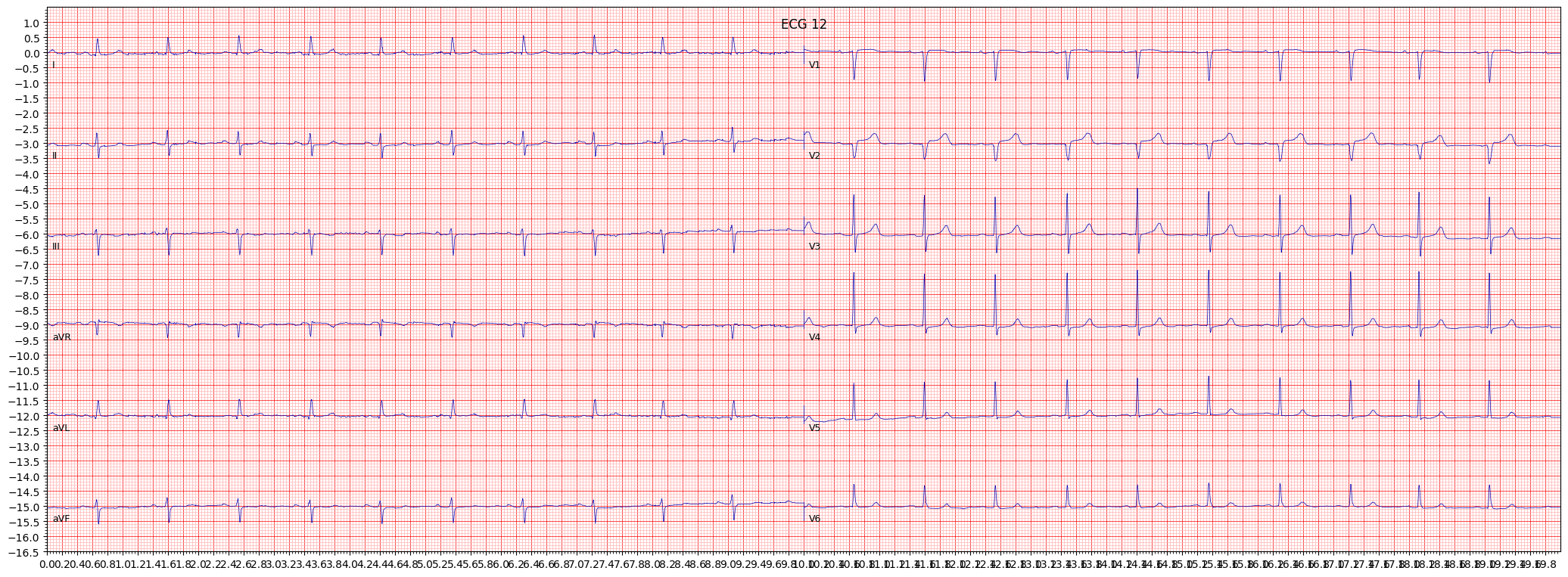 example 8:
example 8:
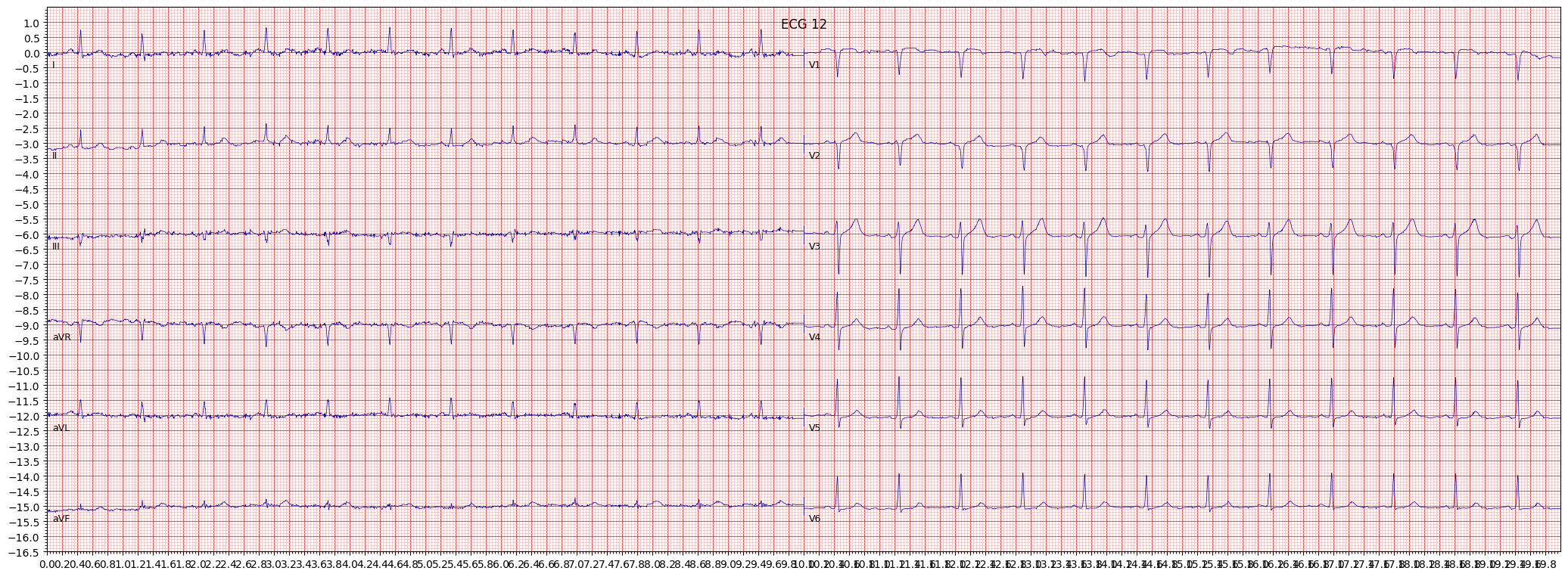 example 9:
example 9:
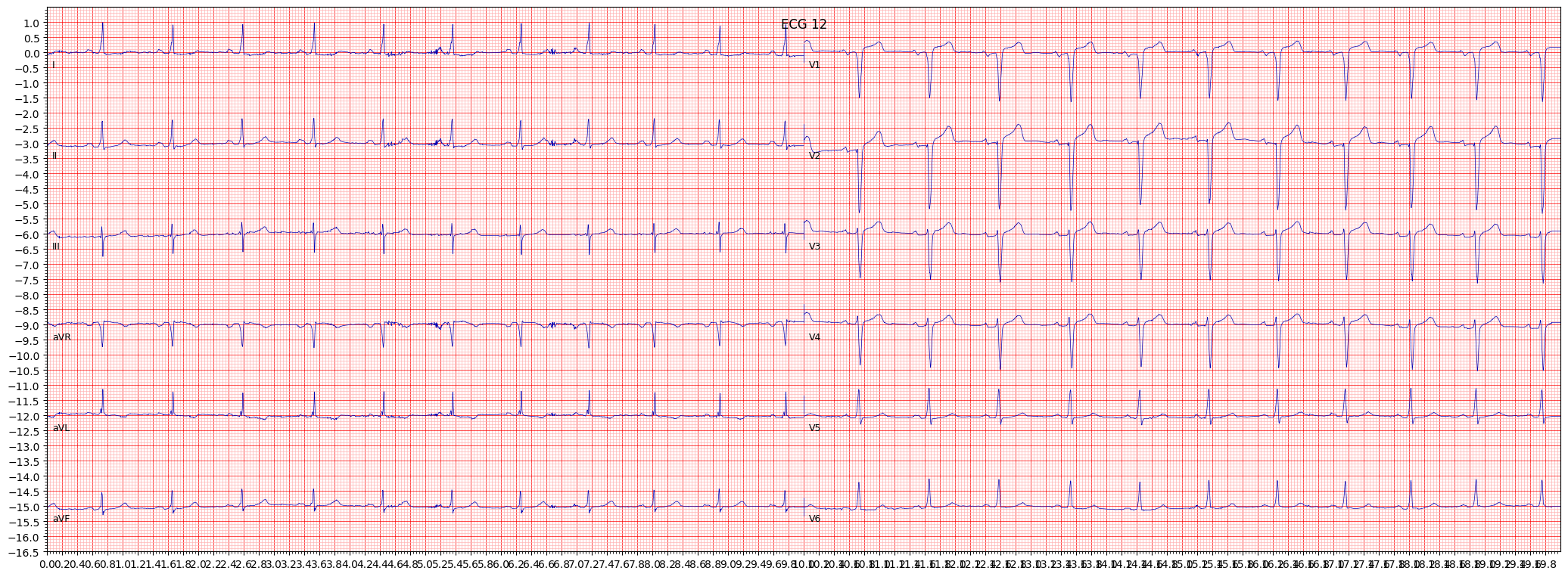 example 10:
example 10: