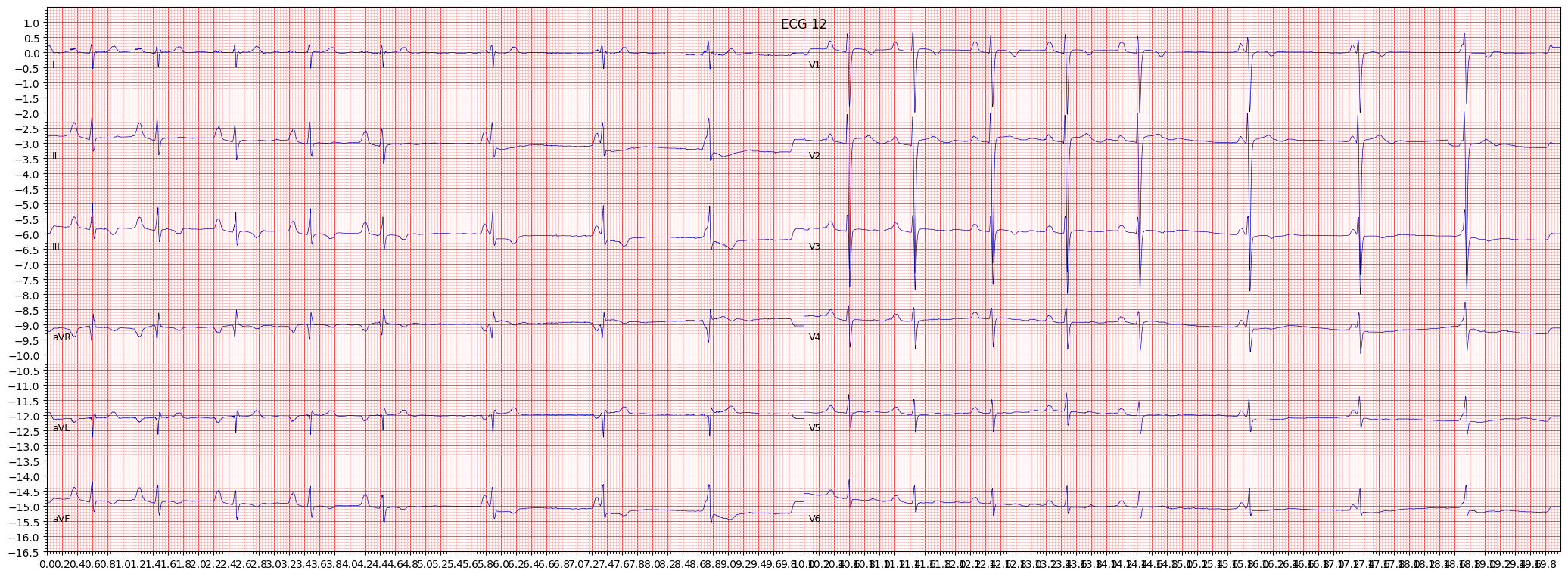
left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)
Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) is a type of electrocardiogram (ECG) finding that indicates an abnormality in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Specifically, LPFB occurs when there is a delay or blockage in the electrical impulses that travel through the left posterior fascicle of the left bundle branch, which is responsible for conducting impulses to the posterior and inferior regions of the left ventricle.
LPFB can be asymptomatic, meaning that the individual may not experience any noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, and dizziness.
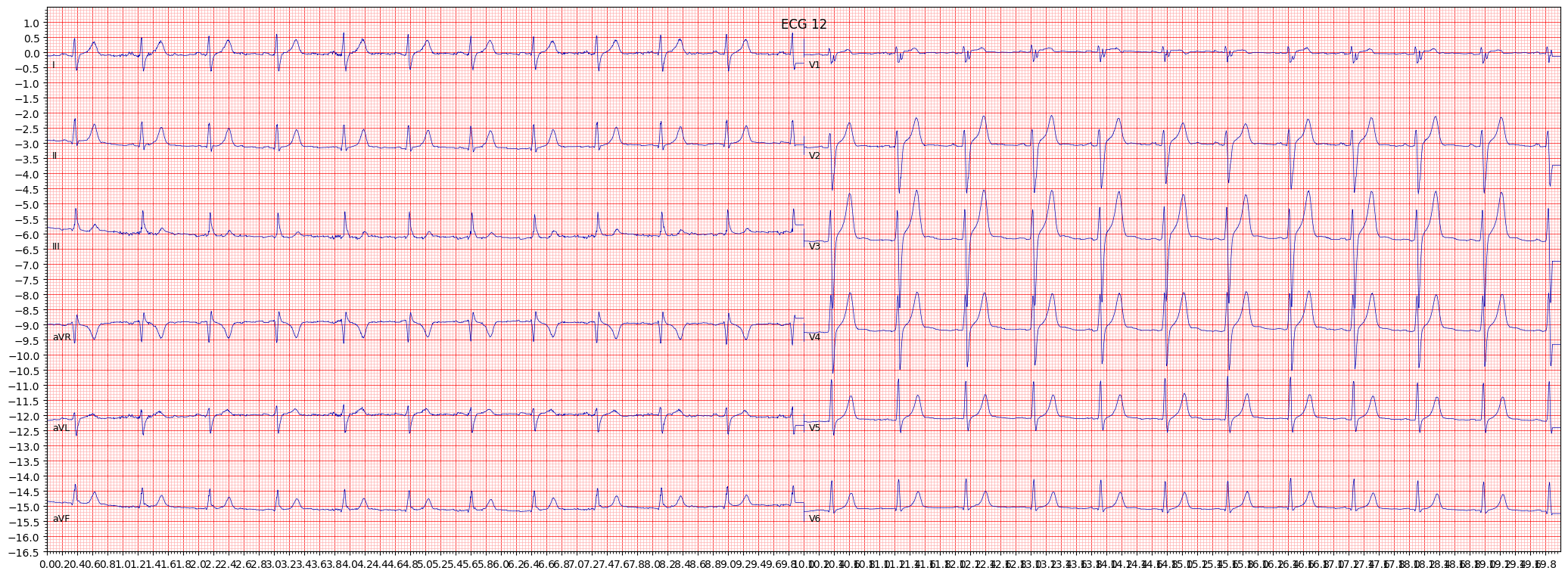
When reviewing an ECG for LPFB, it is important to pay attention to the presence of a right axis deviation, which is greater than 90 degrees. Other things to pay attention to include the presence of qS complexes in leads I and aVL, and the presence of an R wave with a prolonged R wave peak time in leads V1 and V2.
- Look for a right axis deviation (> 90°)
- Check for the presence of qS complexes in leads I and aVL
- Observe the presence of an R wave with a prolonged R wave peak time in leads V1 and V2
If LPFB is suspected, further testing such as echocardiography or cardiac catheterization may be recommended to determine if there is an underlying cardiovascular condition that requires treatment.
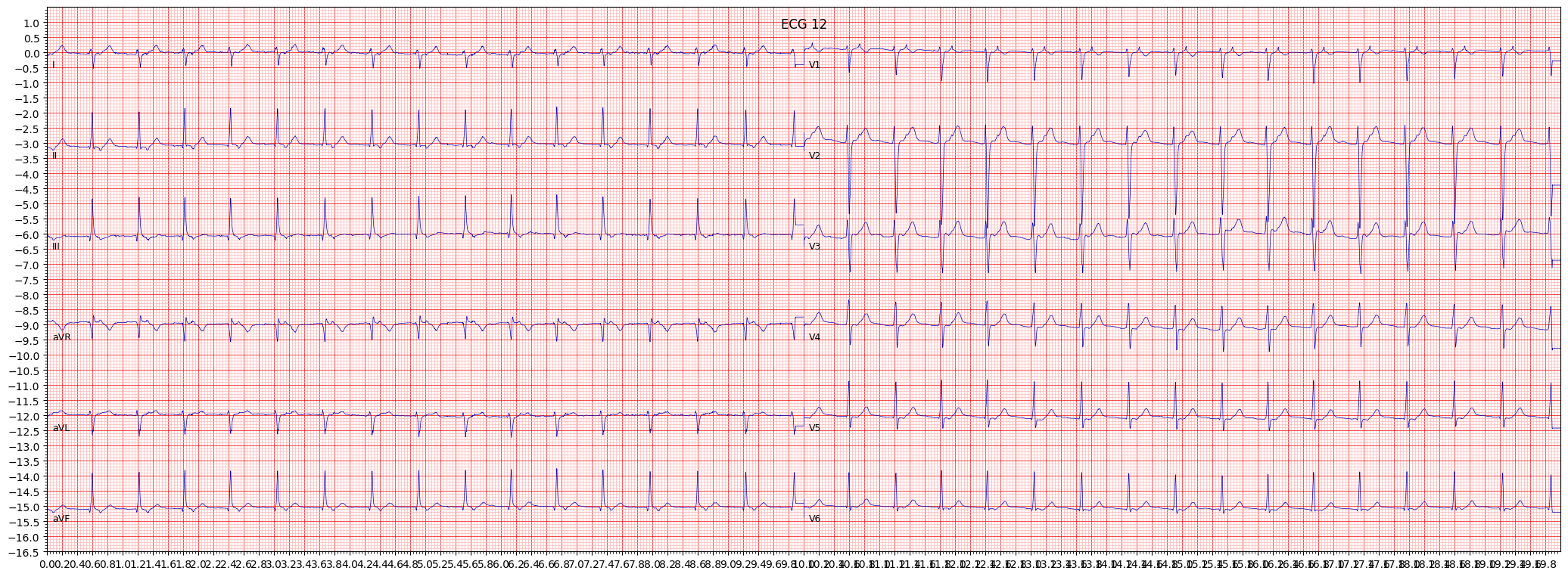 example 2:
example 2:
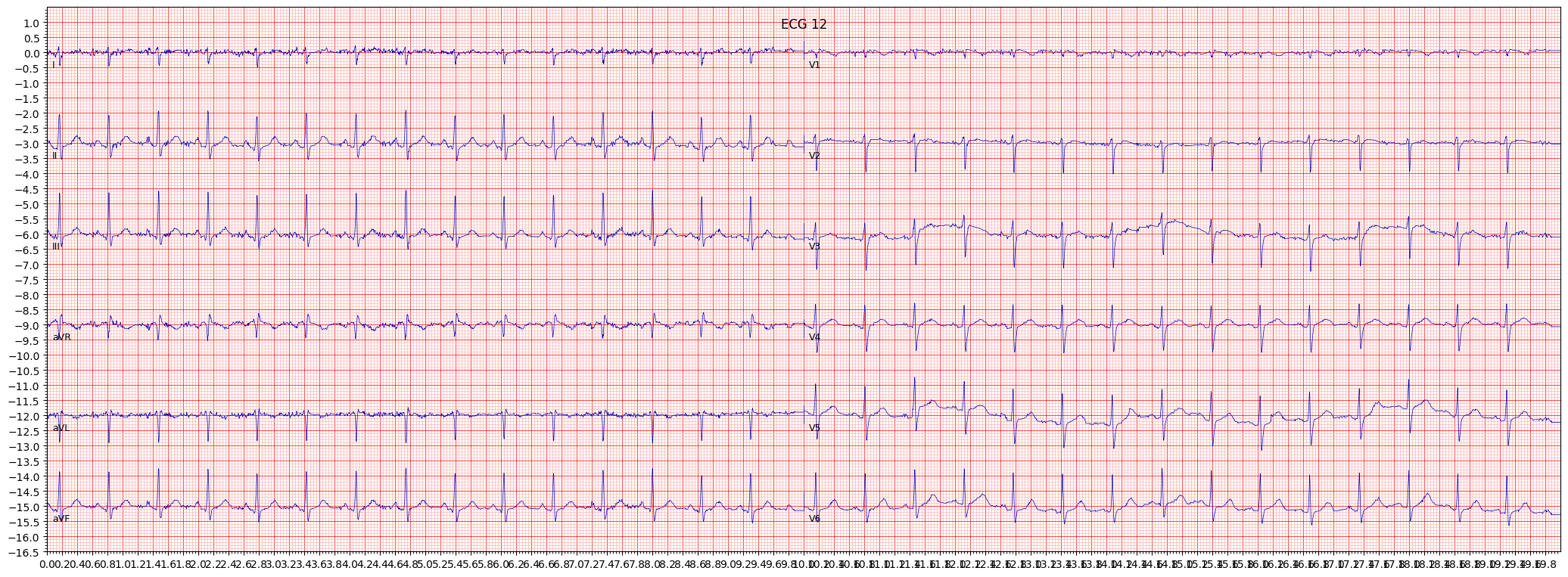 example 3:
example 3:
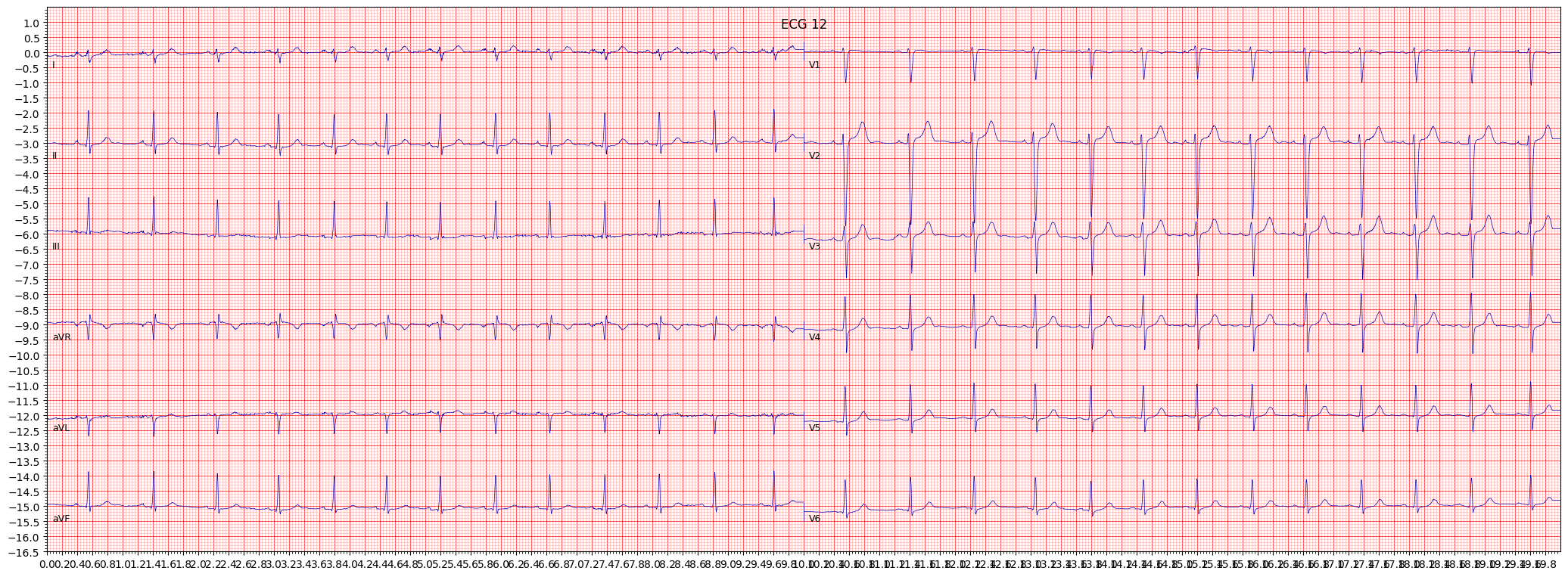 example 4:
example 4:
 example 5:
example 5: