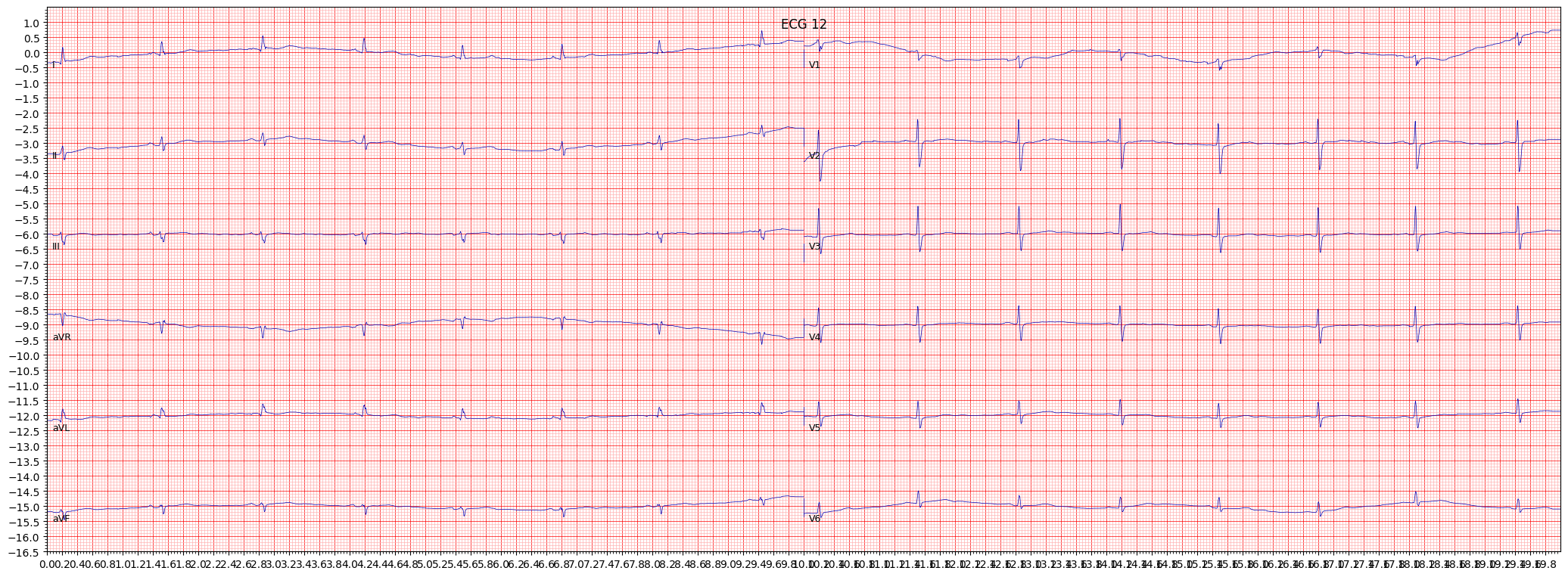
non-diagnostic T abnormalities (NDT)
Non-diagnostic T abnormalities (NDT) on an ECG refer to changes in the T wave, which represents the repolarization of the ventricles of the heart. These changes are considered non-diagnostic because they are not specific enough to indicate a certain cardiac condition or disease.
Common causes of NDT include medication use, electrolyte imbalances, physical activity, and stress. In some cases, NDT may be a normal variation and not require any treatment or intervention.
When reviewing an ECG for NDT, it is important to pay attention to the morphology of the T wave, including the amplitude, duration, and symmetry. Other things to pay attention to include the presence of other abnormalities, such as ST segment or Q wave abnormalities.
- Look for changes in the morphology of the T wave, including amplitude, duration, and symmetry
- Check for the presence of other abnormalities, such as ST segment or Q wave abnormalities
If NDT is identified on an ECG, further evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying cause and determine if any treatment or intervention is necessary. This may include additional testing, such as blood tests or imaging studies, and management of any underlying conditions or risk factors.
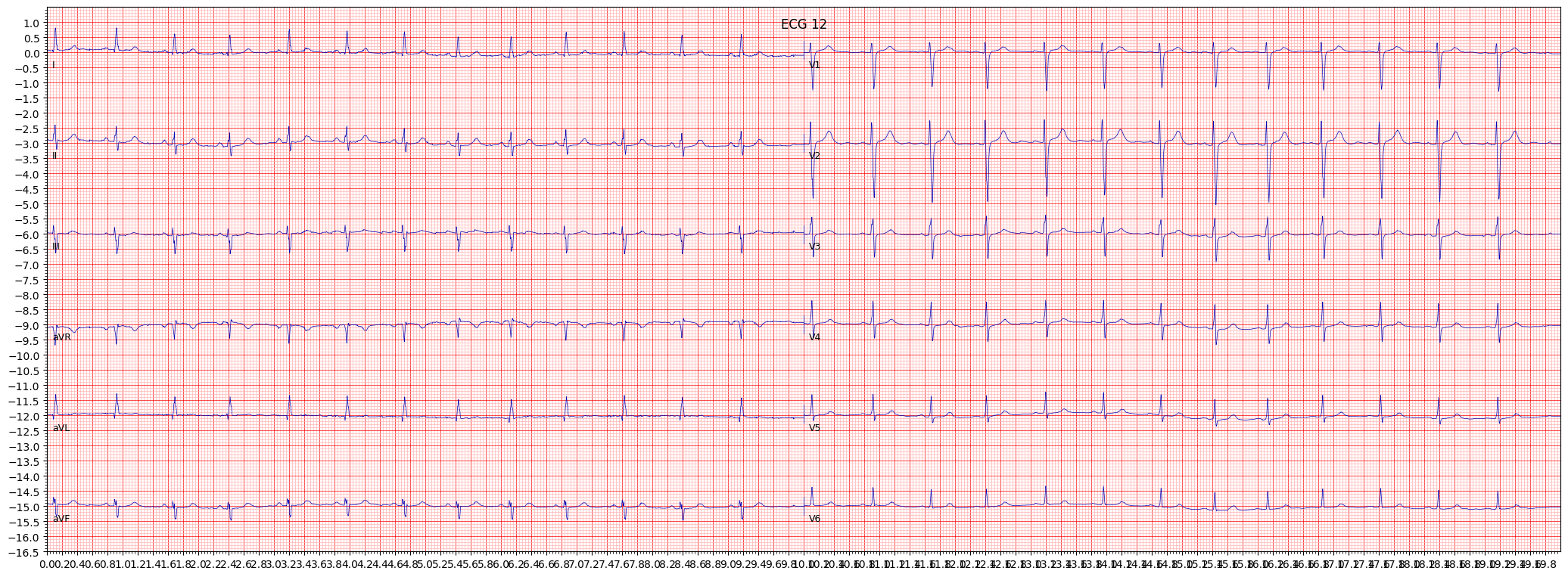 example 2:
example 2:
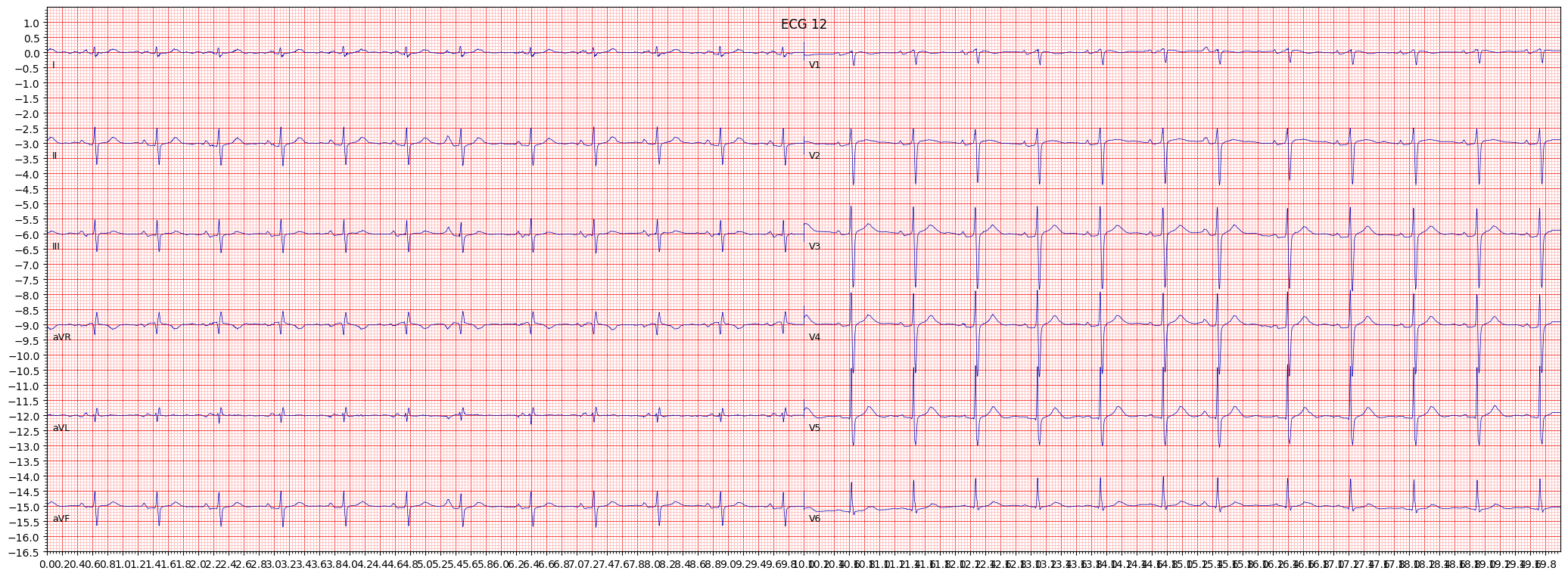 example 3:
example 3:
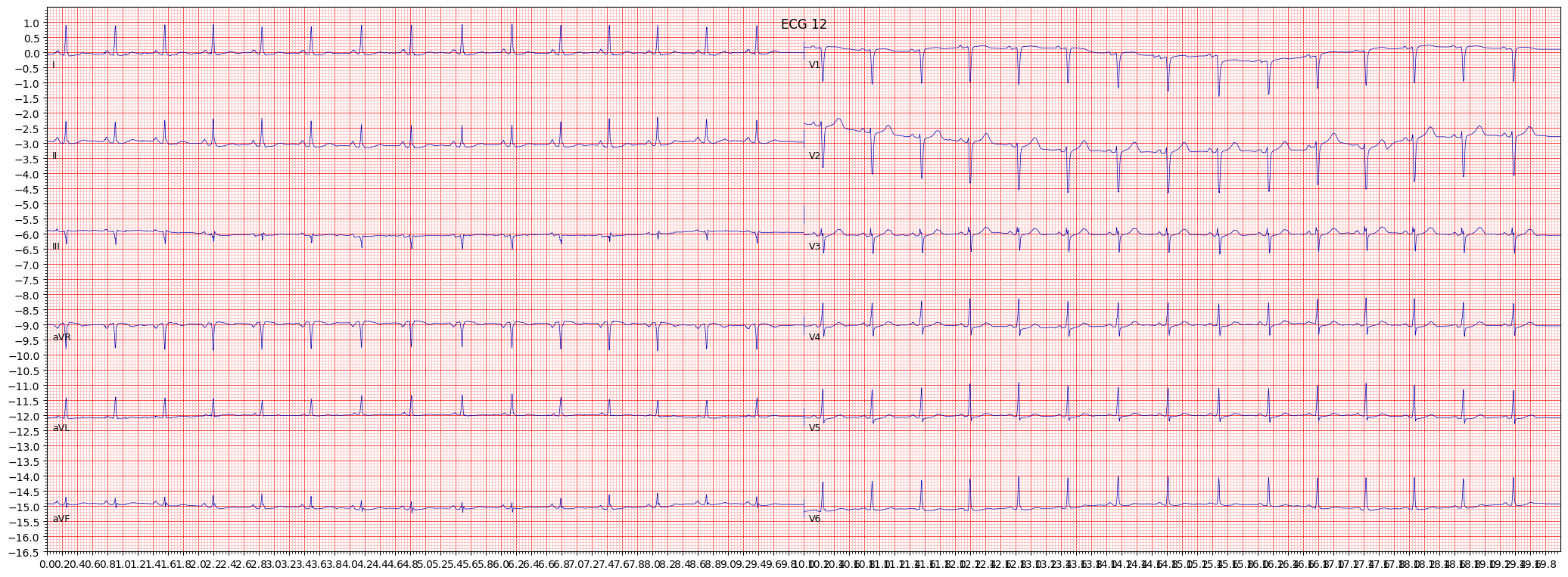 example 4:
example 4:
 example 5:
example 5:
 example 6:
example 6:
 example 7:
example 7:
 example 8:
example 8:
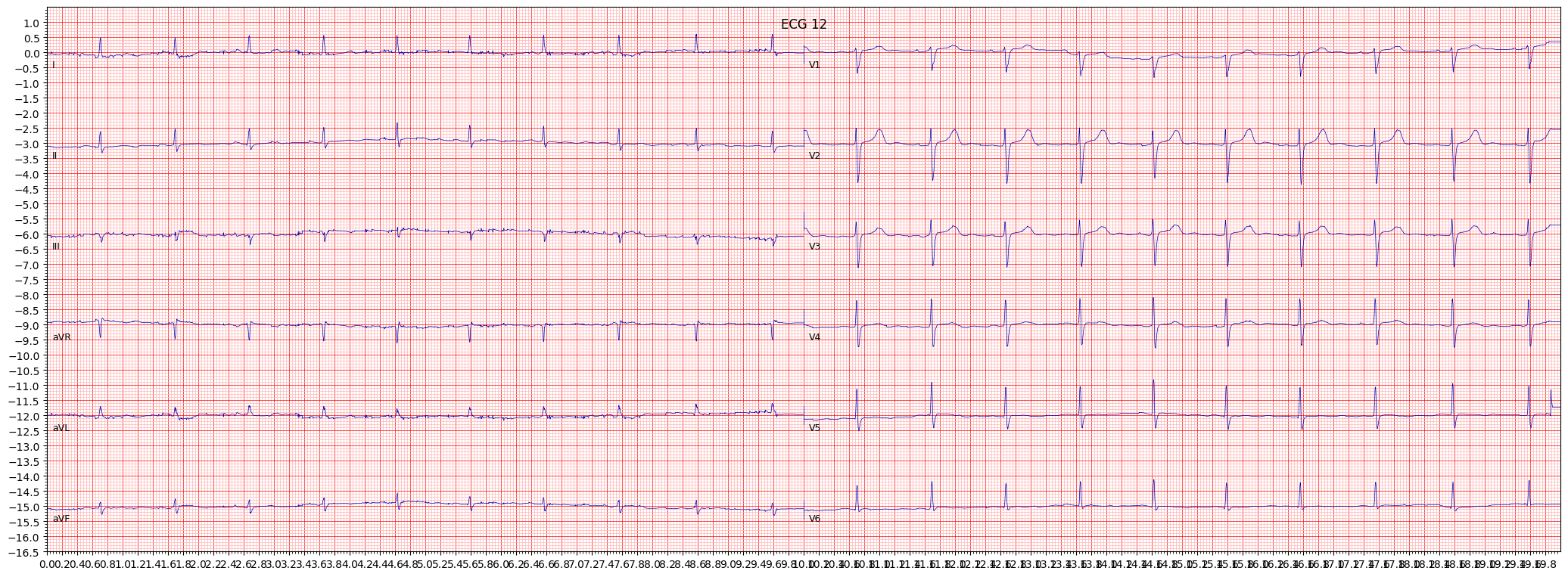 example 9:
example 9:
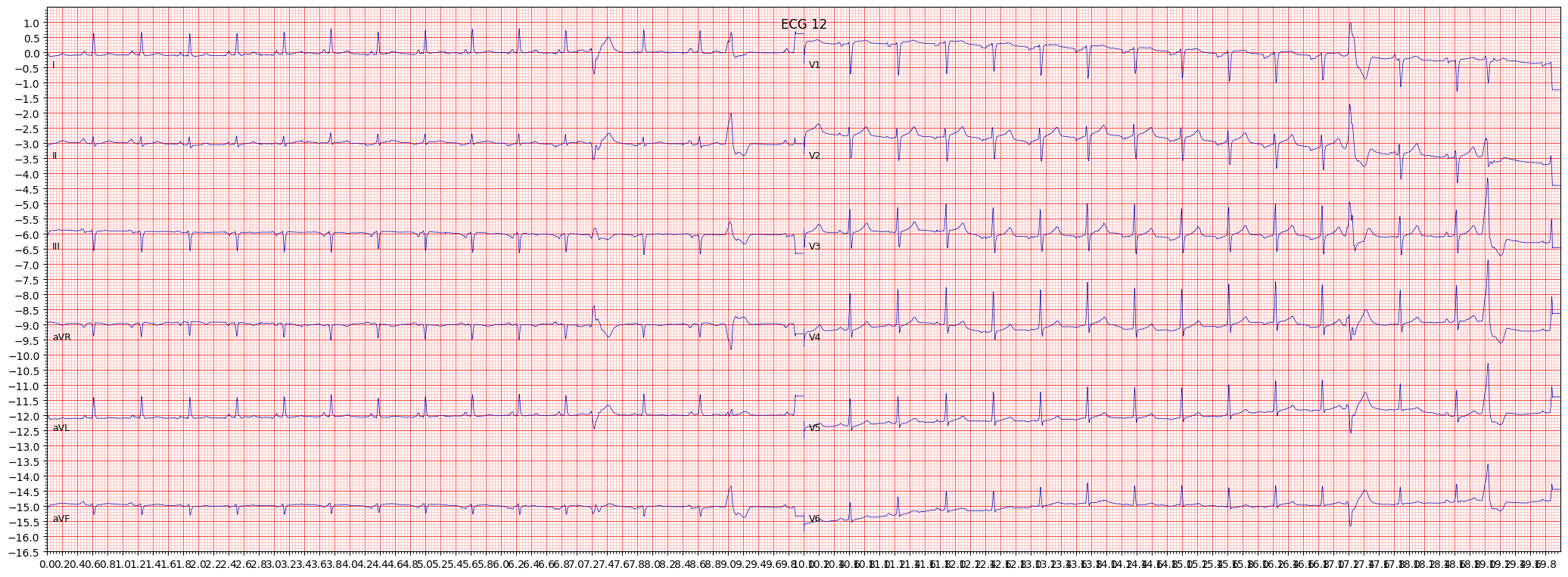 example 10:
example 10: