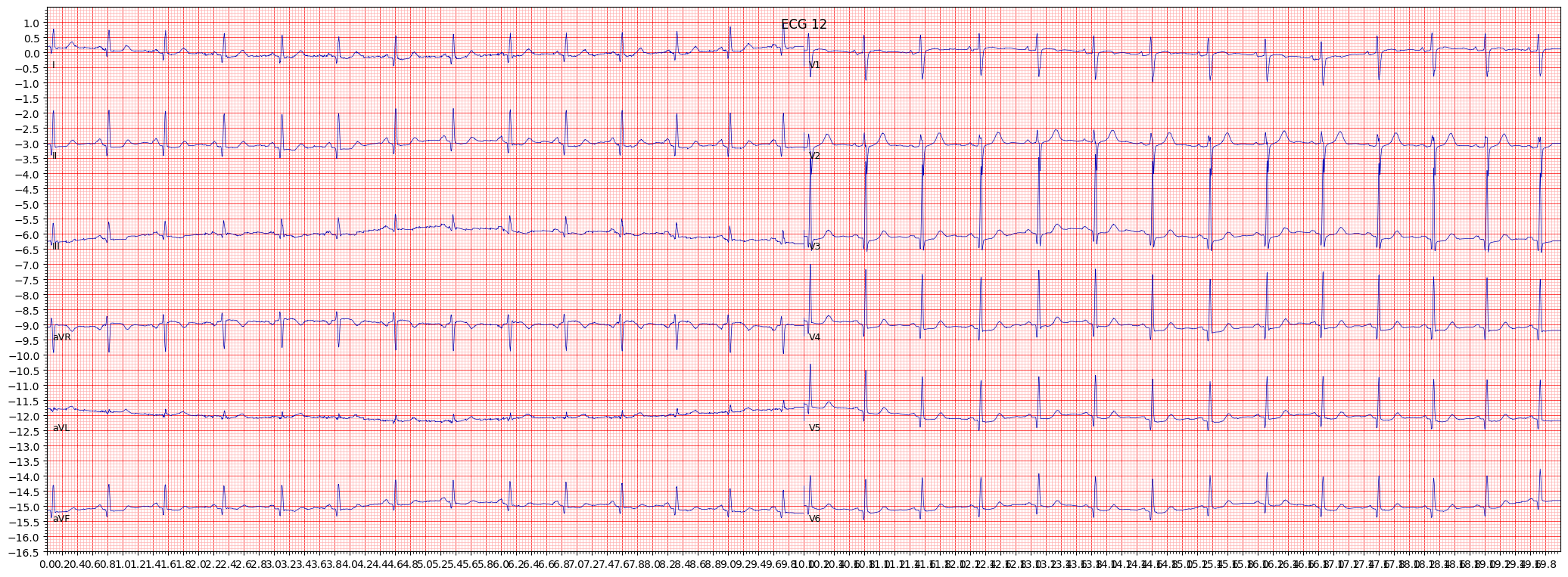
septal hypertrophy (SEHYP)
Septal hypertrophy (SEHYP) is a condition that occurs when the muscle of the septum, which is the wall that separates the left and right ventricles of the heart, thickens. This can be a response to long-standing high blood pressure or other cardiovascular conditions.
Common symptoms of SEHYP include shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, and dizziness. However, some individuals may not experience any symptoms.
When reviewing an ECG for SEHYP, it is important to pay attention to the amplitude and duration of the QRS complex, as well as the presence of ST segment and T wave abnormalities. Other things to pay attention to include the presence of left axis deviation and the presence of pathological Q waves in the septal leads.
- Look for an increased amplitude and duration of the QRS complex
- Check for the presence of ST segment and T wave abnormalities
- Observe the presence of left axis deviation
- Look for the presence of pathological Q waves in the septal leads
If SEHYP is suspected, further testing such as echocardiography or cardiac MRI may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the hypertrophy. Treatment may include medications such as antihypertensives to manage high blood pressure and other cardiovascular conditions.
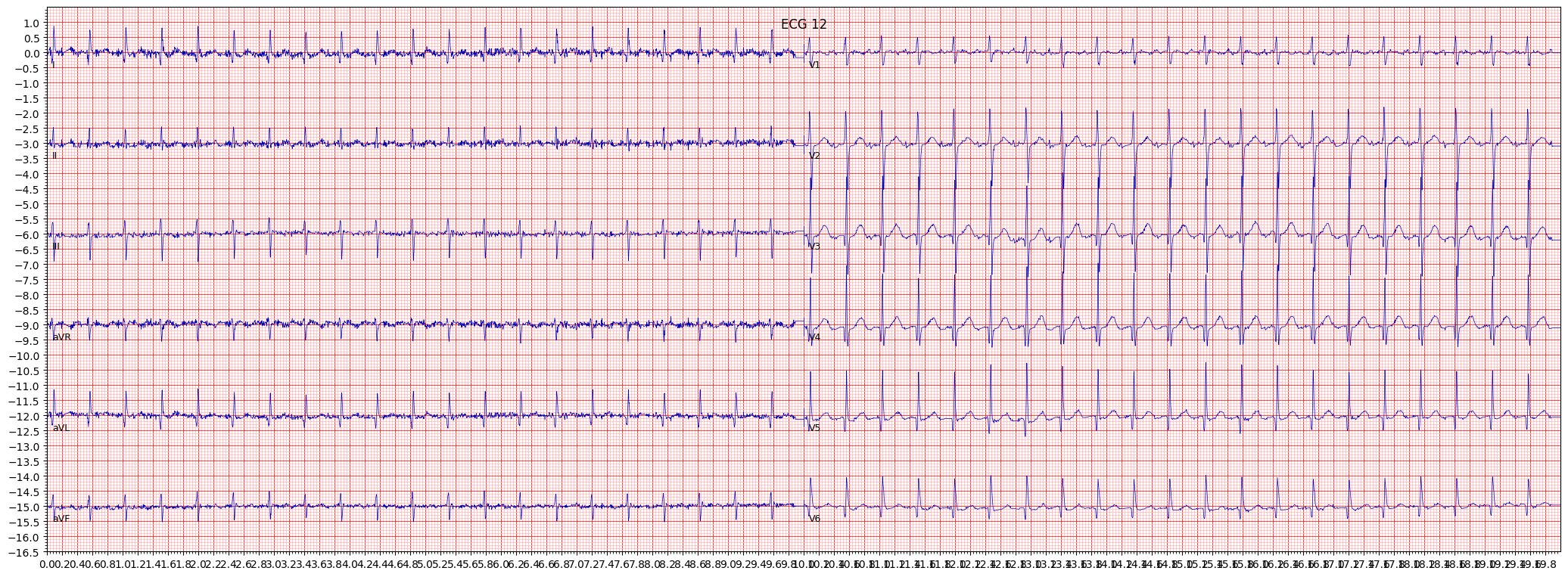 example 2:
example 2:
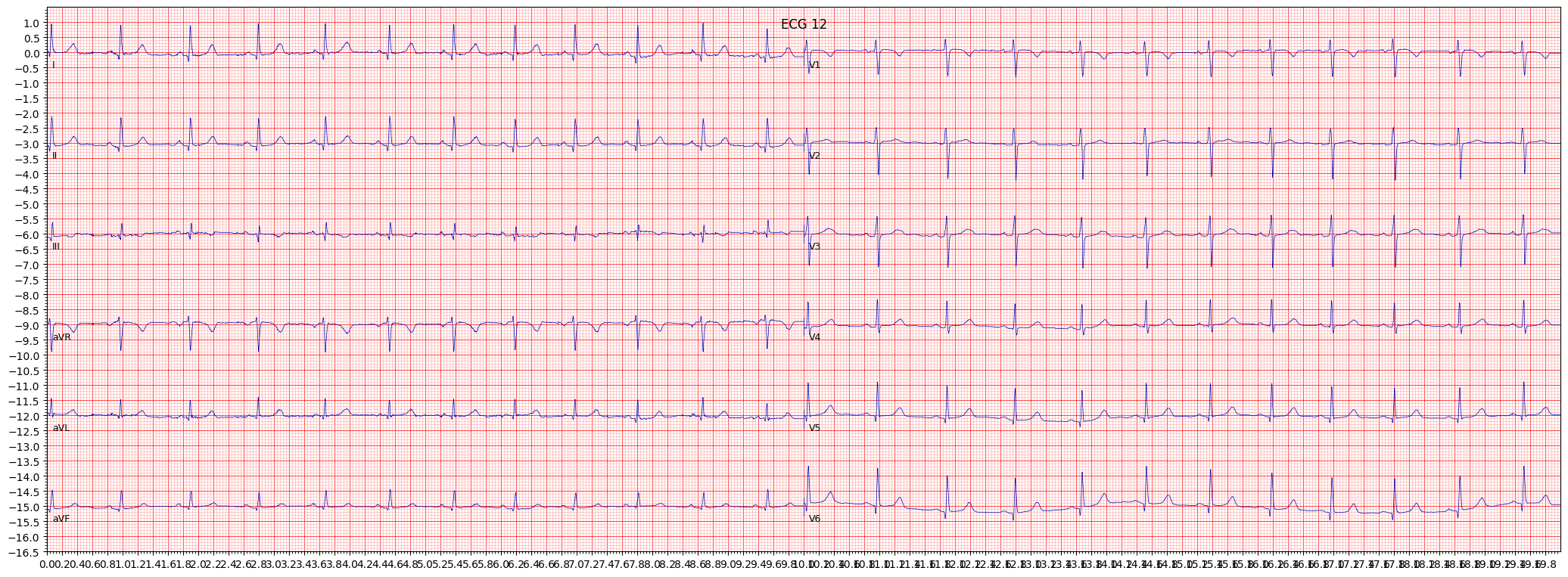 example 3:
example 3: